Science doesn’t always follow common sense. Some discoveries appear more like fiction than fact. But the natural world, space, and living organisms often defy expectations. What seems impossible is sometimes well documented. These science facts might sound unlikely at first, but each one is backed by research. Get ready to explore the stranger side of science.
1. Bananas Are Slightly Radioactive

Bananas contain potassium, and a small part of that potassium is radioactive. It is not enough to harm you, but technically, eating a banana adds a tiny amount of radiation to your body. There is even something called the “banana equivalent dose,” which scientists use to explain how harmless certain levels of radiation are. It may sound strange, but it is a real teaching tool.
2. Space Smells Like Burnt Steak

Astronauts returning from spacewalks often report a strange smell lingering on their suits. It has been described as seared steak or hot metal. That scent comes from high-energy particles reacting with the materials on the spacesuit. While you cannot smell anything in space directly, this leftover scent gives a surprising glimpse into what space might really be like.
3. Wombat Poop Is Cube-Shaped
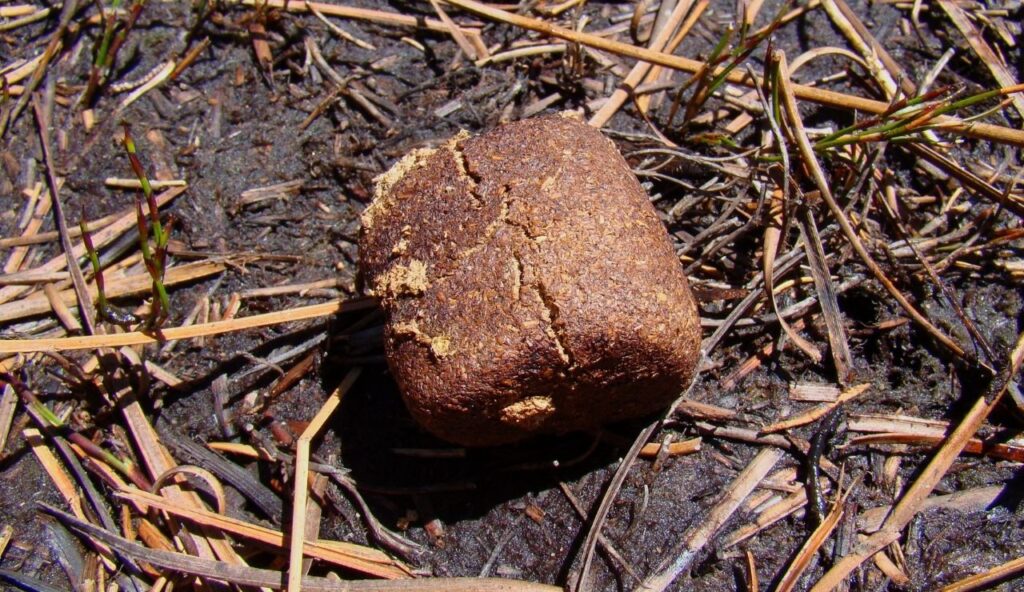

Wombats, which are short-legged marsupials from Australia, produce poop in the shape of cubes. This unusual shape keeps the droppings from rolling away, which helps them mark their territory. Scientists believe the cube form comes from the way the wombat’s intestines stretch and contract. It may sound like a fictional detail, but it is completely accurate.
4. Octopuses Have Three Hearts
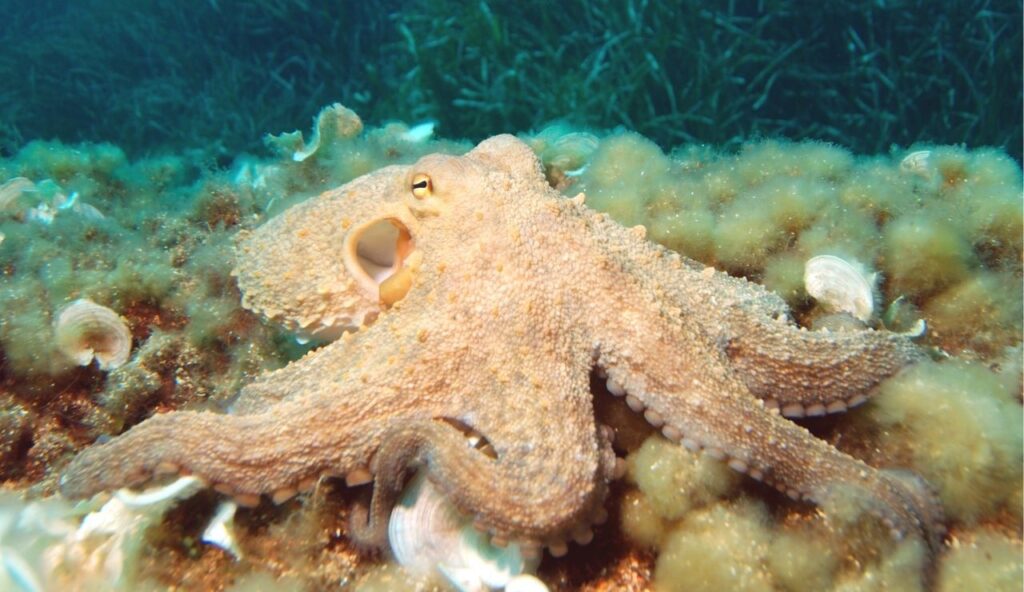

An octopus has not one, but three hearts. Two of them pump blood to the gills, while the third sends it to the rest of the body. When the octopus swims, the main heart temporarily stops. That is one reason why these animals prefer crawling over swimming. Their blood is also blue, due to a copper-based molecule. Many aspects of their biology are unexpected.
5. Your Stomach Gets a New Lining Every Few Days
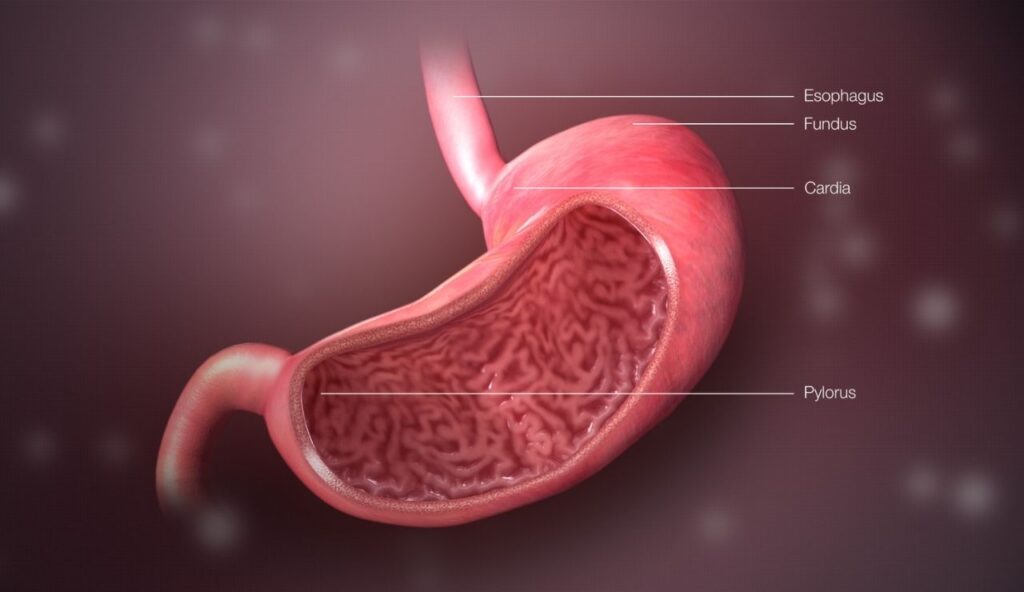
The inside of your stomach is constantly breaking down and rebuilding. This is because stomach acid is strong enough to dissolve tissue, so your body replaces the lining every few days to protect itself. Without this ongoing repair, the acid would damage your organs. It is a continuous process that keeps digestion running safely without you noticing.
6. A Day on Venus Is Longer Than Its Year
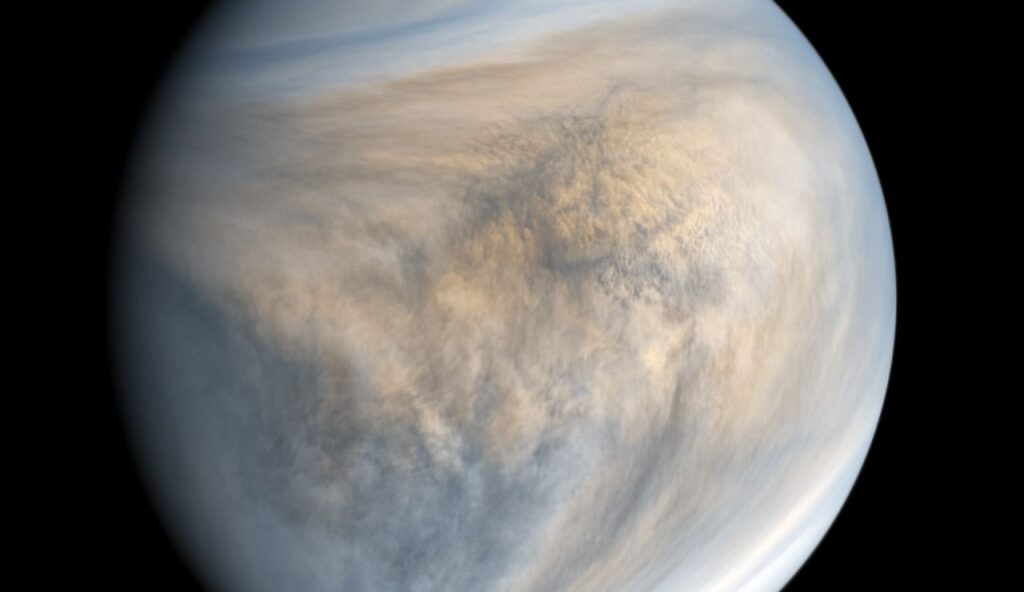

Venus rotates so slowly that one full day there lasts about 243 Earth days. Meanwhile, its orbit around the Sun takes about 225 Earth days. That means a day on Venus is longer than a year. The planet’s rotation is slow and moves in the opposite direction of most planets. This fact is well documented by space agencies that have studied Venus for decades.
7. Sloths Can Hold Their Breath Longer Than Dolphins
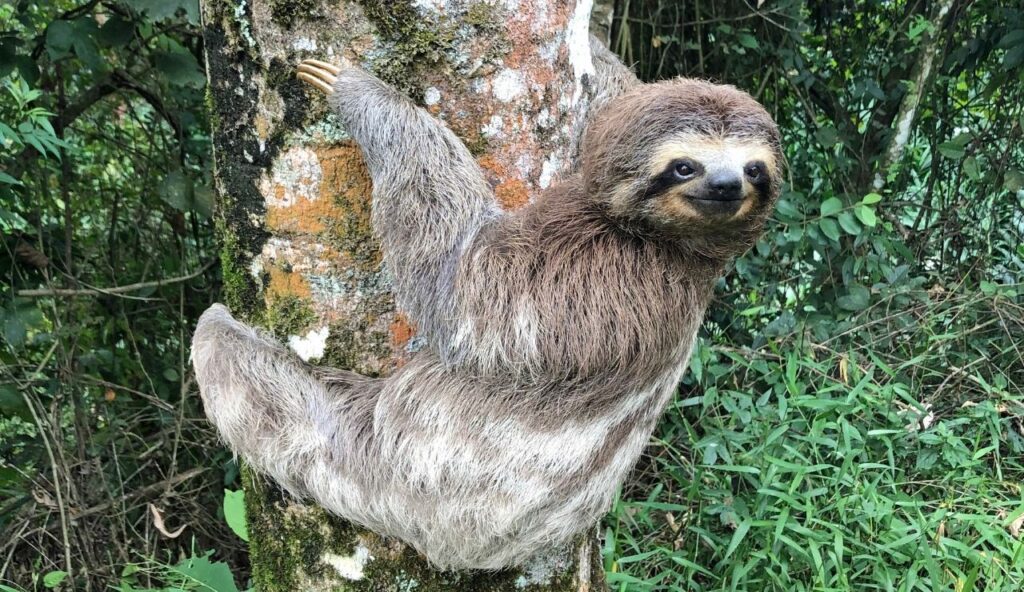

A sloth can slow its heart rate and hold its breath underwater for up to 40 minutes. Dolphins, in comparison, typically surface every 10 to 15 minutes. Sloths do not live in water, but this ability helps them survive when crossing rivers or avoiding predators. It is a surprising advantage for an animal known for its slow movements and calm behavior.
8. There’s a Jellyfish That Can Live Forever
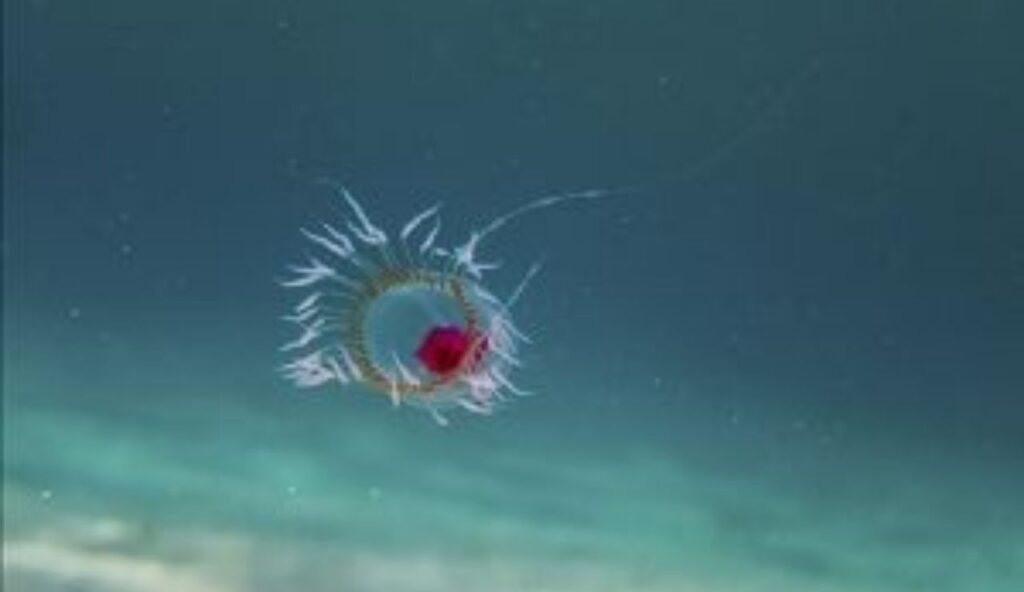

The species Turritopsis dohrnii is often referred to as the immortal jellyfish. When stressed or injured, it can return to an earlier stage of life and repeat its life cycle. This ability allows it to avoid death from aging. While it is not immune to all dangers, it challenges what scientists once thought was possible in the natural world.
9. The Eiffel Tower Grows in Summer
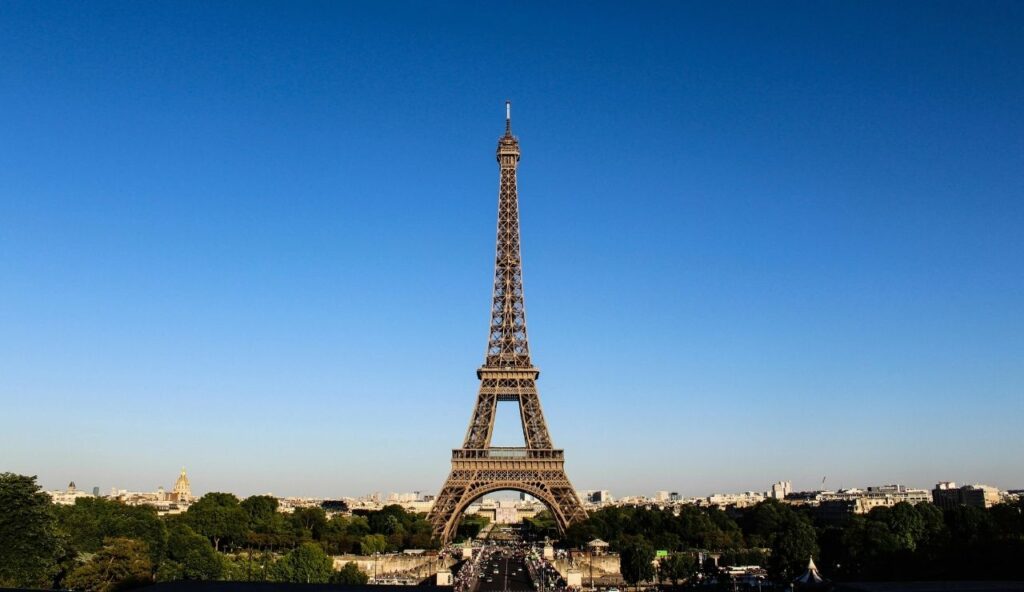

During hot weather, the metal in the Eiffel Tower expands and causes the structure to grow taller by several inches. As temperatures rise, the iron stretches slightly, increasing the tower’s height. Once the weather cools, it shrinks back to its original size. This change is a real-life example of how heat can affect solid structures.
10. Saturn Could Float in Water
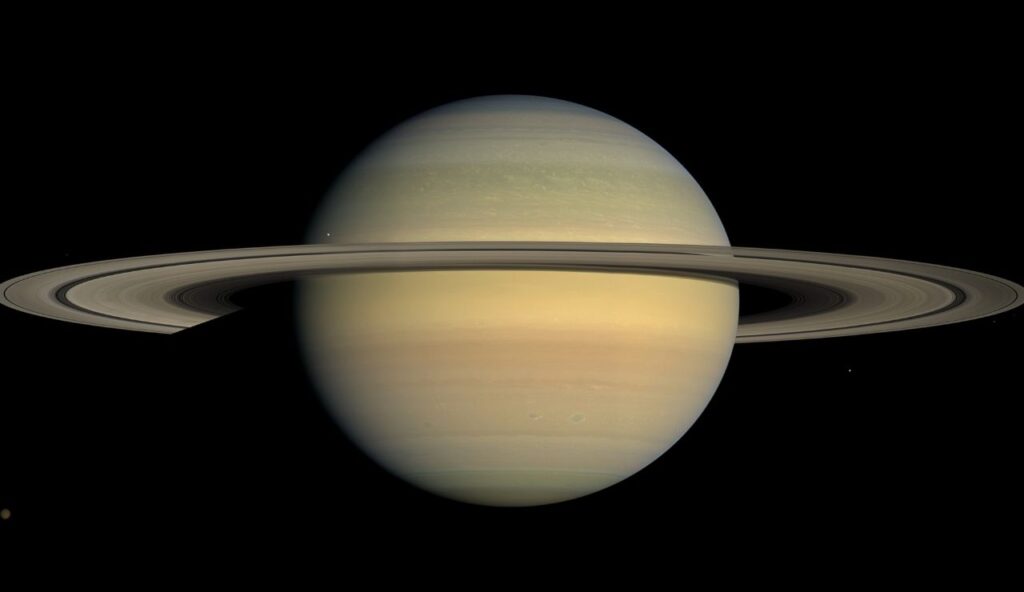
Saturn is made mostly of gases and is less dense than water. If there were a body of water large enough, Saturn would float. This comparison helps explain how light the planet really is. While it is only a theoretical scenario, the measurements behind it are accurate. The idea of a floating planet may seem far-fetched, but it is based on real science.
11. Spiders Can Use Their Silk to Fly
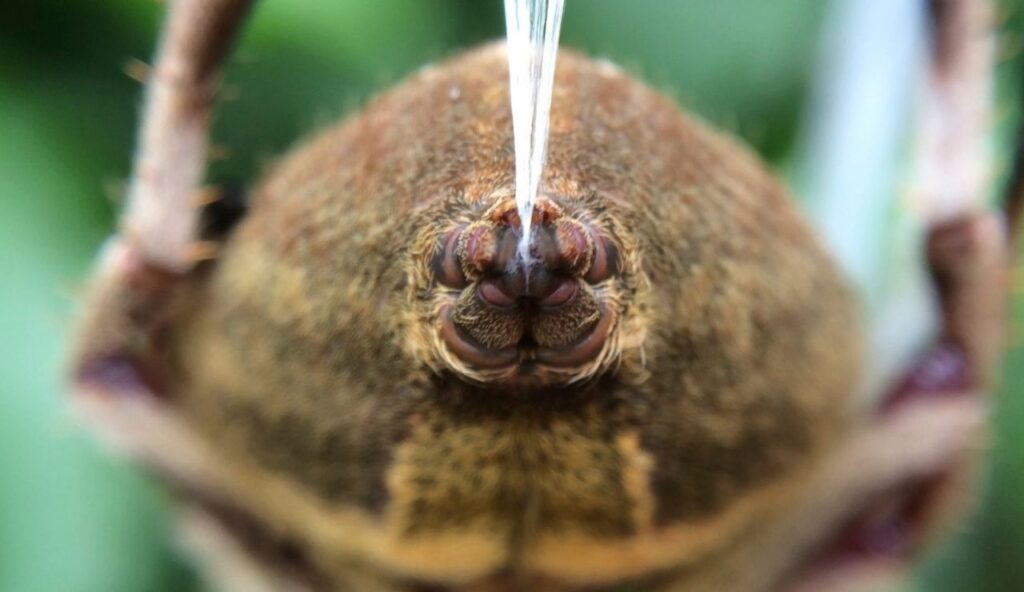

Certain spiders can release silk into the air and catch wind currents, allowing them to travel long distances. This behavior is called ballooning. Some spiders have been found hundreds of miles from land, carried entirely by air. This method helps them find new habitats and escape threats. It is a well-observed behavior that still surprises many scientists.
12. Earth’s Rotation Is Gradually Slowing Down

The Earth does not spin at a fixed speed. Due to tidal friction caused by the Moon, the rotation slows very slightly over time. This means that days are becoming longer, though the change is gradual. During the age of the dinosaurs, one full day lasted closer to 23 hours. Scientists continue to measure this effect using precise instruments that track changes over long periods.
13. Water Can Boil and Freeze at the Same Time
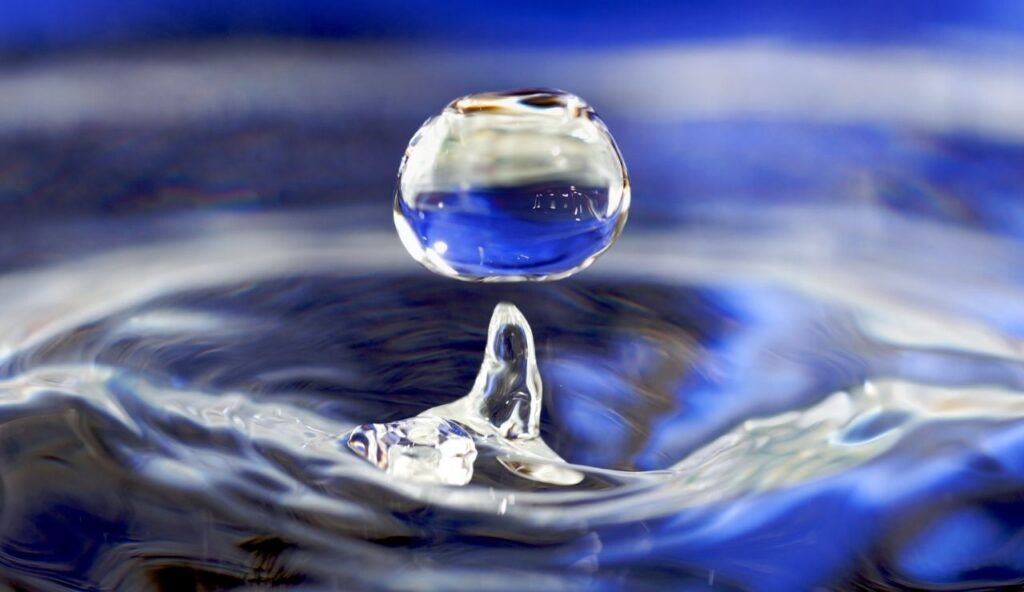

At a very specific temperature and pressure, known as the triple point, water can exist as a solid, liquid, and gas at once. This condition is rare in nature but can be demonstrated in laboratory settings. It provides valuable insight into how substances behave under different conditions. Though it seems contradictory, the triple point is a well-documented scientific fact.
14. Birds Are the Closest Living Relatives to Dinosaurs
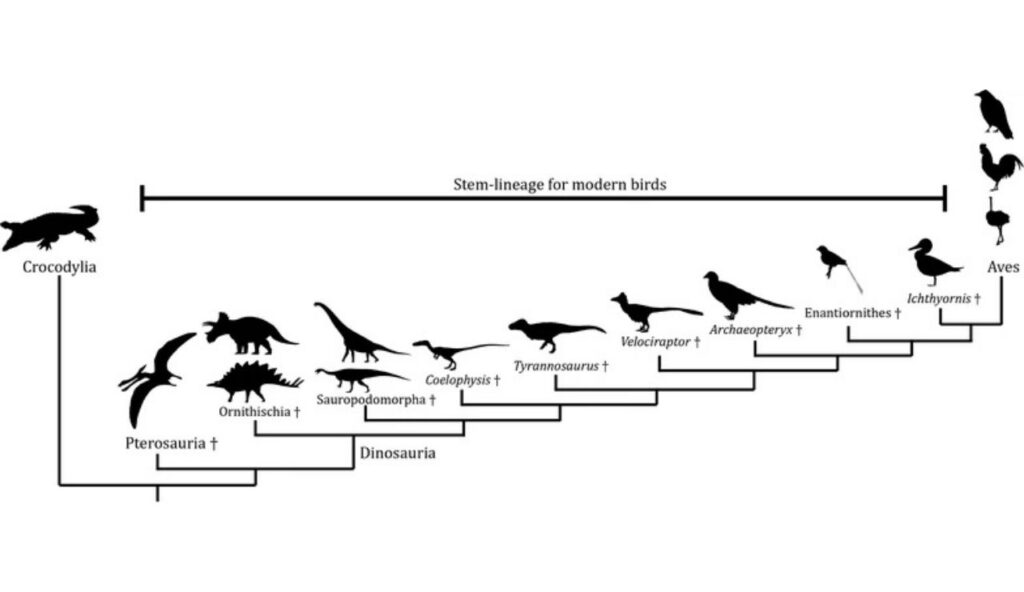
Modern birds are direct descendants of a group of two-legged dinosaurs known as theropods. Traits like feathers, egg-laying, and certain skeletal structures can be traced back to these prehistoric creatures. Fossil records and genetic analysis have confirmed this link. This evolutionary relationship has reshaped our understanding of both birds and dinosaurs.
15. The Average Cloud Weighs Over a Million Pounds
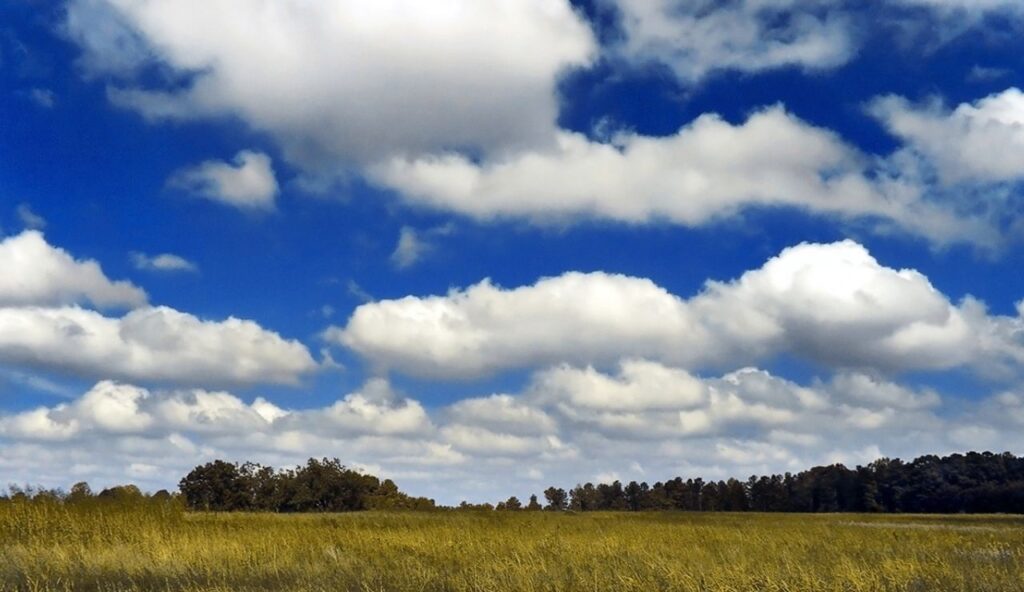

A single cumulus cloud may look weightless, but it contains large quantities of water vapor. Scientists estimate that the average cloud holds over one million pounds of water. This mass is supported by rising air currents that keep the water droplets suspended. Despite its visual appearance, a cloud is a heavy structure made possible by physics and atmospheric conditions.