Some empires did more than just conquer land. They shaped the world in ways we still experience today. These powerful civilizations built cities, created trade routes, influenced languages, and brought distant cultures together. Their reach stretched across continents, leaving behind legacies that still matter. If you’re curious about the biggest players in world history, this list is the perfect place to start.
1. The British Empire

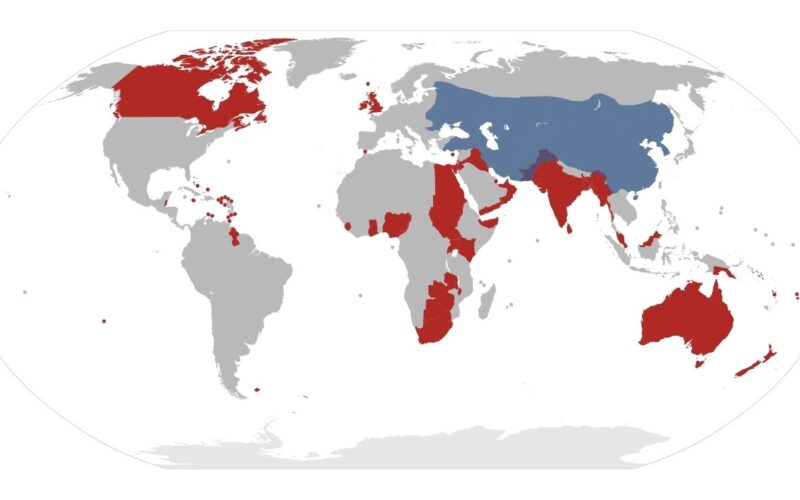
At its height, the British Empire ruled about a quarter of the world’s population and land. It had control over regions in Asia, Africa, the Americas, and Oceania. The saying that the sun never sets on the British Empire was true for a reason. Its reach was global, and its legacy is still visible in language, law, and culture across many countries. No other empire matched its land coverage.
2. The Mongol Empire
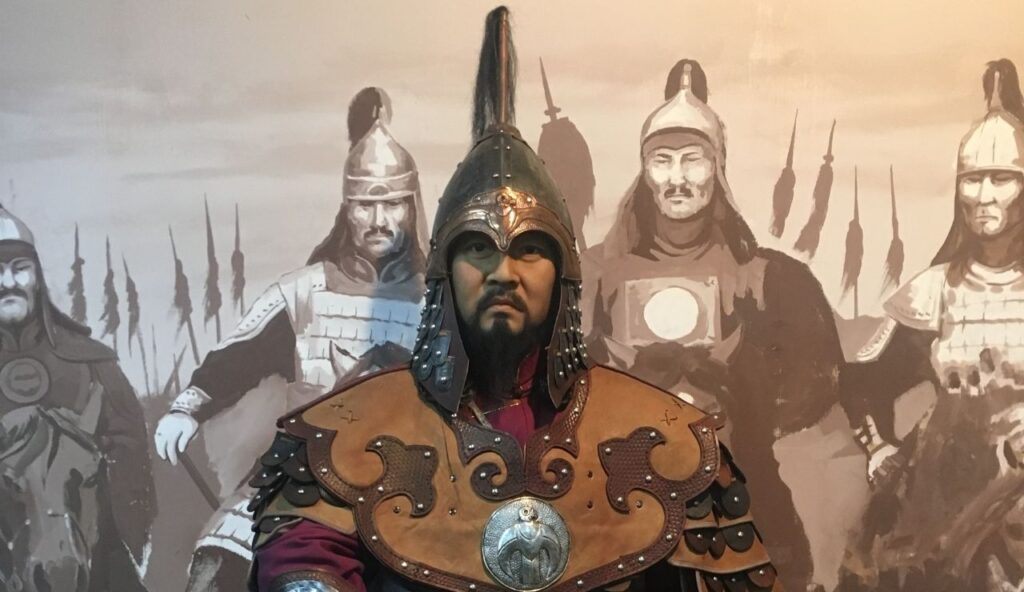

The Mongol Empire rose quickly under the leadership of Genghis Khan and became the largest connected land empire in history. It stretched from Eastern Europe to East Asia, covering parts of modern-day China, Russia, and the Middle East. Despite their fearsome reputation, the Mongols also boosted trade and cultural exchange along the Silk Road, helping ideas and goods move across continents.
3. The Russian Empire
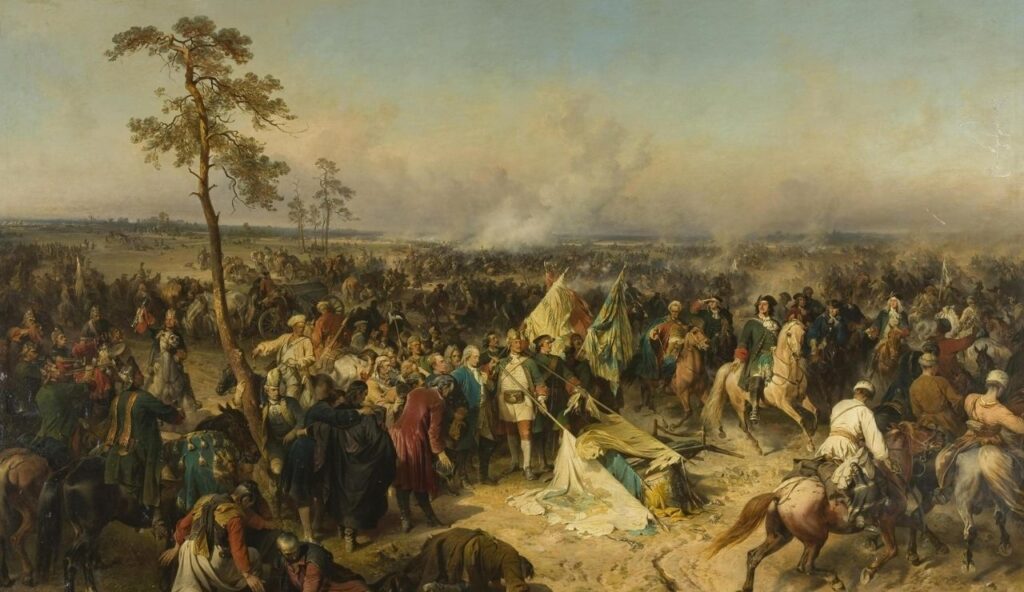

Before the Soviet Union, there was the Russian Empire. It expanded across Eastern Europe, Siberia, and into parts of Central Asia and North America. By the early 1900s, it was one of the largest empires ever by land area. Known for its powerful tsars and dramatic revolutions, the empire shaped the history of Eurasia. Its influence can still be felt in the region’s politics and culture today.
4. The Spanish Empire
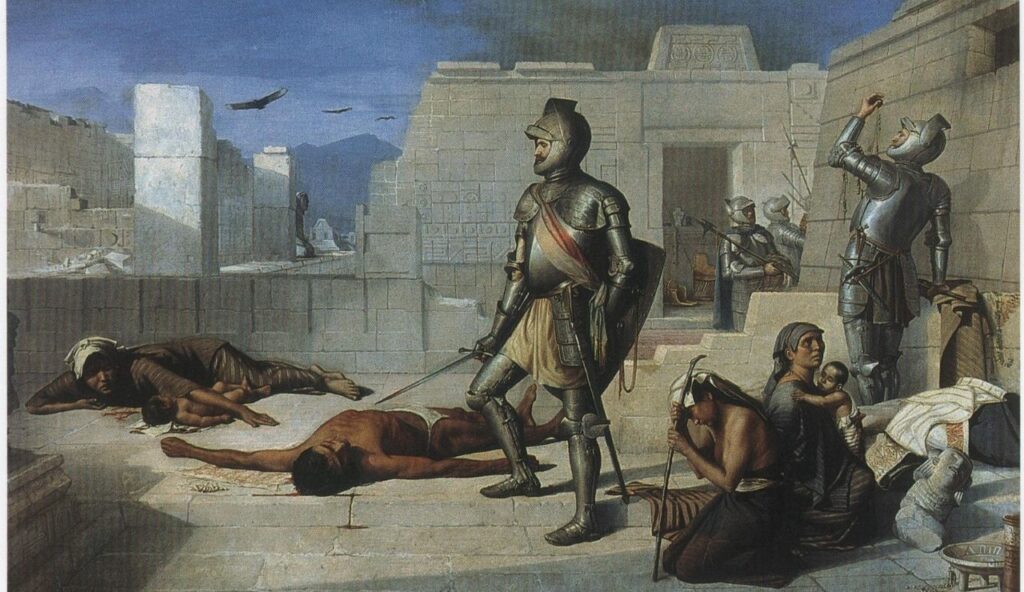

The Spanish Empire was one of the first truly global empires, reaching across Europe, the Americas, Africa, and Asia. After Columbus’s voyage, Spain claimed huge parts of the New World, including most of South and Central America. It also had colonies in the Philippines and parts of Africa. This empire spread the Spanish language and culture across continents, leaving a lasting mark on history.
5. The Ottoman Empire
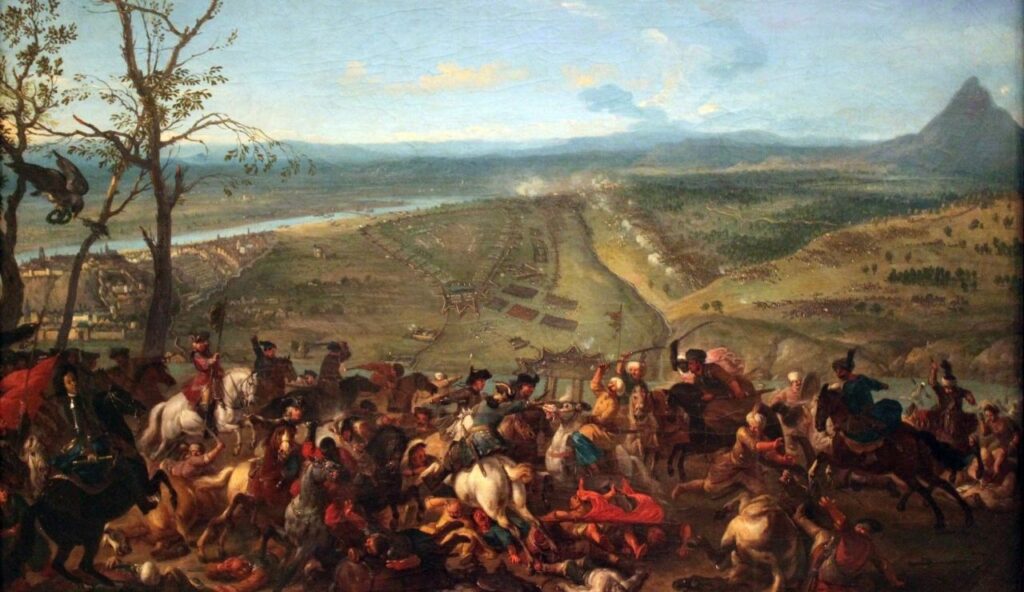

The Ottoman Empire lasted over 600 years and covered parts of Europe, Asia, and Africa. It was centered in what is now Turkey, with its capital in Istanbul. At its peak, it controlled lands from Hungary to the Arabian Peninsula. The empire blended cultures and religions, becoming a major force in both politics and art. It played a huge role in shaping the modern Middle East and Eastern Europe.
6. The Qing Dynasty
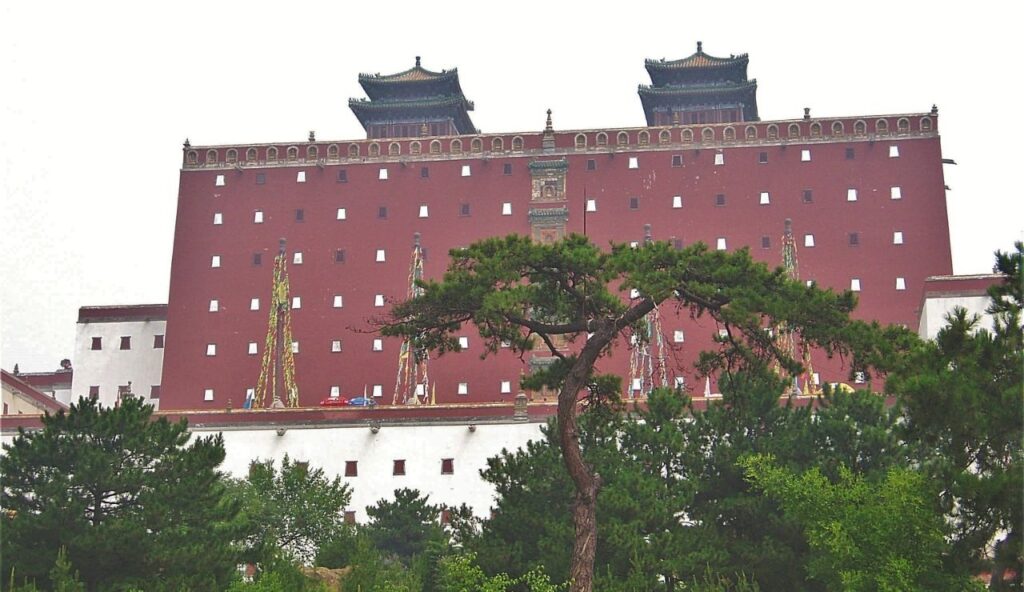

The Qing Dynasty was the last imperial dynasty of China and one of the largest empires in Asian history. It ruled from the mid-1600s to the early 1900s, covering not only China but also Tibet, Mongolia, and Taiwan. The Qing expanded China’s borders more than any dynasty before it. Despite facing internal struggles and foreign pressures, it remained powerful for over two centuries.
7. The Roman Empire
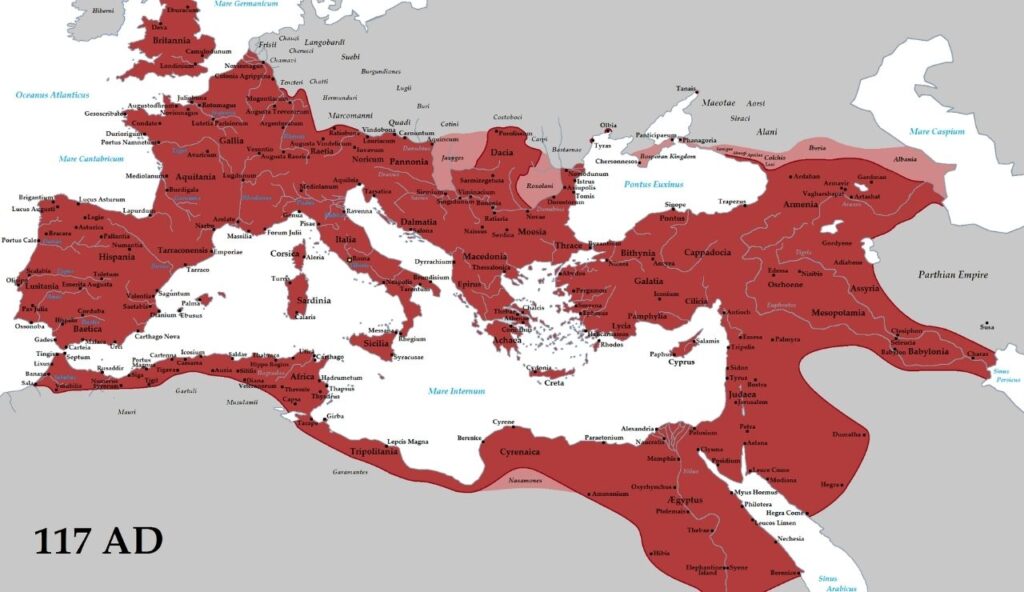
The Roman Empire ruled much of Europe, North Africa, and parts of the Middle East for centuries. It started as a small city-state and grew into a massive empire known for roads, architecture, and law. Latin, its main language, still influences modern languages today. Even after its fall, Roman ideas about government and engineering continued to shape the Western world for generations.
8. The Umayyad Caliphate
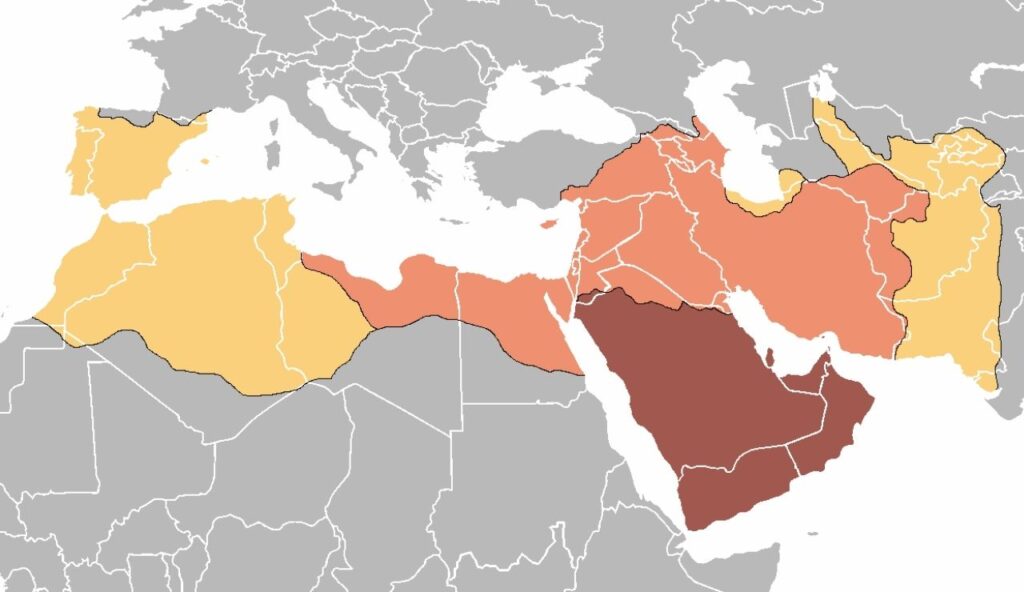
The Umayyad Caliphate was one of the largest Islamic empires and stretched from Spain in the west to India in the east. It grew rapidly in the 7th and 8th centuries, uniting a vast region under a shared religion and language. The caliphate helped spread science, math, and culture across continents. Its capital, Damascus, became a major center of learning and trade during its rule.
9. The French Colonial Empire

The French Colonial Empire was one of the world’s largest, with territories in North America, Africa, Southeast Asia, and the Caribbean. At its peak, it spanned more than ten million square kilometers. France spread its language, laws, and culture far beyond Europe. Many former colonies still speak French today, showing how deeply the empire shaped global history and identity.