Quantum physics isn’t just complex, it’s rewriting reality. As scientists dive deeper into the quantum world, they’re uncovering theories that challenge everything we thought we knew about space, time, and matter. These five cutting-edge concepts aren’t just mind-bending; they’re laying the groundwork for future technologies, redefining how we understand the universe, and forcing us to question what’s truly “real.”
1. Quantum Entanglement
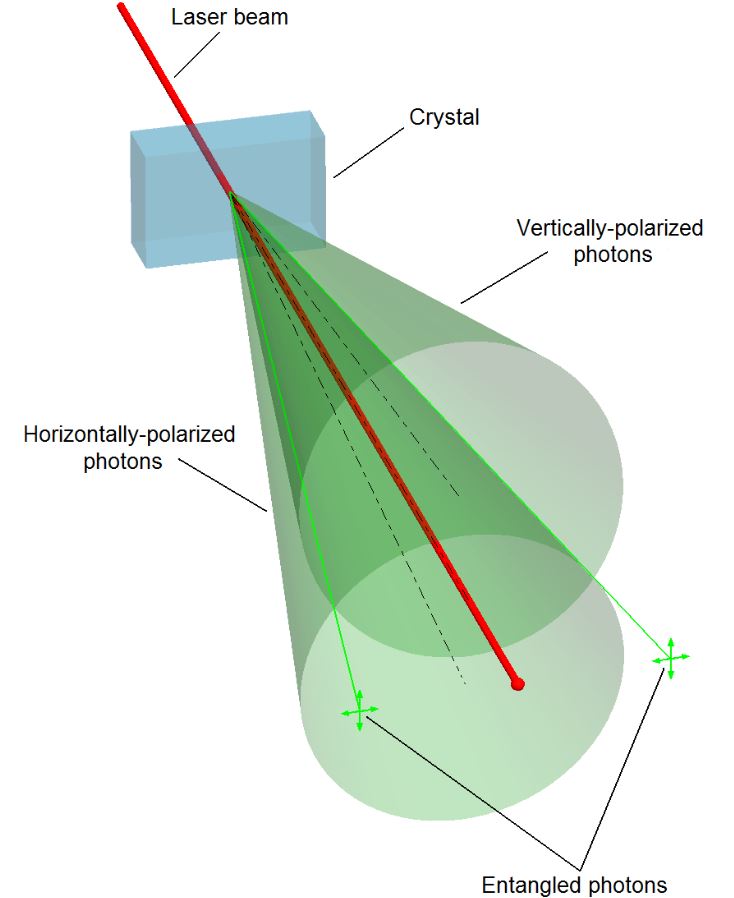
Einstein called it “spooky action at a distance,” but quantum entanglement is very real. When two particles become entangled, their states remain connected, no matter how far apart they are. Measuring one instantly affects the other. This strange connection defies classical physics and is now being used to develop ultra-secure communication and quantum computing systems. It’s a foundational mystery at the heart of quantum mechanics.
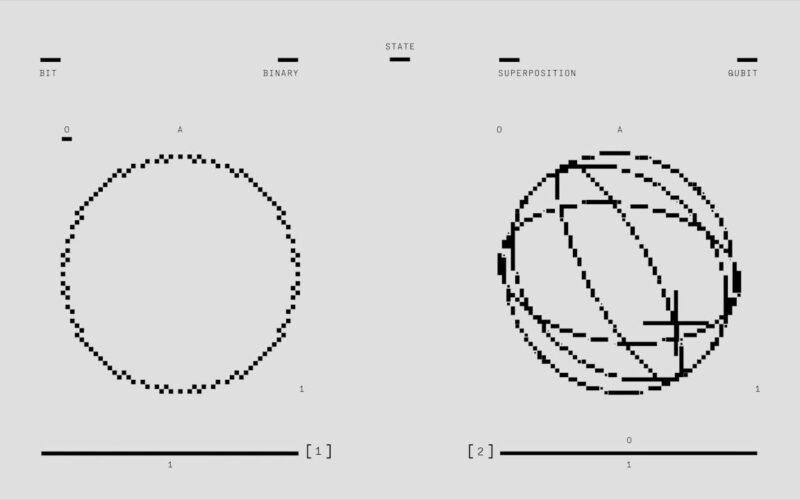
2. Superposition

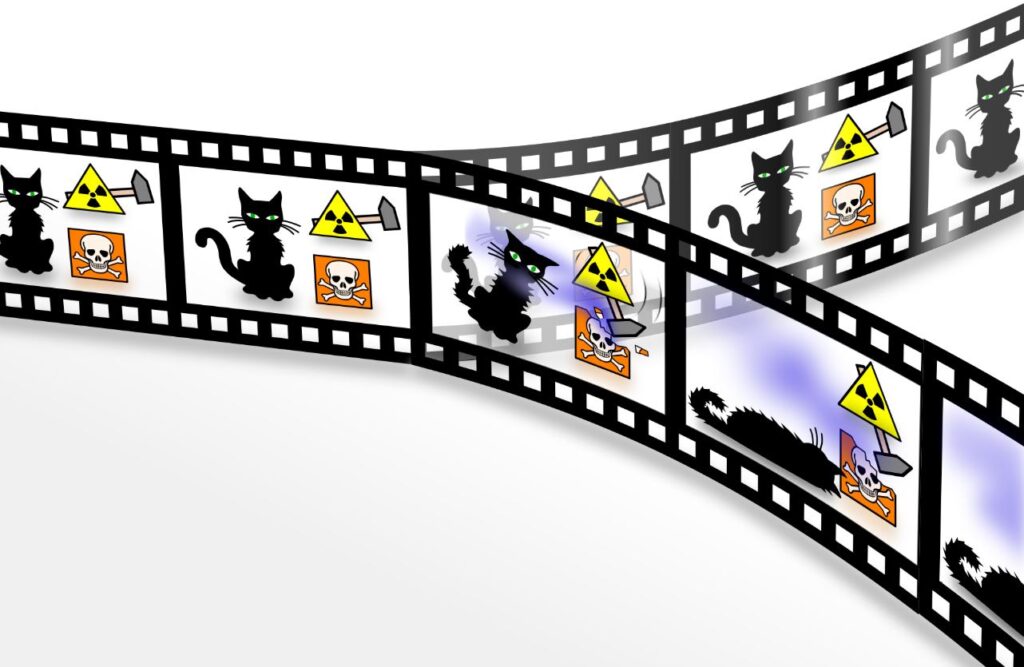
In the quantum world, particles can exist in multiple states at once, a concept called superposition. Think of Schrödinger’s cat, both alive and dead until observed. Superposition allows quantum computers to process vast amounts of data simultaneously, far beyond what classical computers can handle. It challenges our understanding of reality, where observing something might actually change what it is or how it behaves.
3. Quantum Loop Gravity
Quantum loop gravity is a theory aiming to unite quantum mechanics and general relativity. Unlike string theory, it doesn’t rely on extra dimensions. Instead, it proposes that space itself is made of tiny loops, forming a kind of quantum “fabric.” This idea could explain black hole behavior and the origins of the universe. If proven, it might bring us closer to a unified theory of everything.
4. Many Worlds Interpretation
Forget one timeline, what if every possibility actually happens? The many worlds interpretation suggests that every quantum decision splits the universe into new realities. Each time a particle behaves one way or another, a new world is born. This theory eliminates the need for “collapse” when observing quantum states and opens wild possibilities for parallel universes, where countless versions of reality coexist.
5. Quantum Field Theory
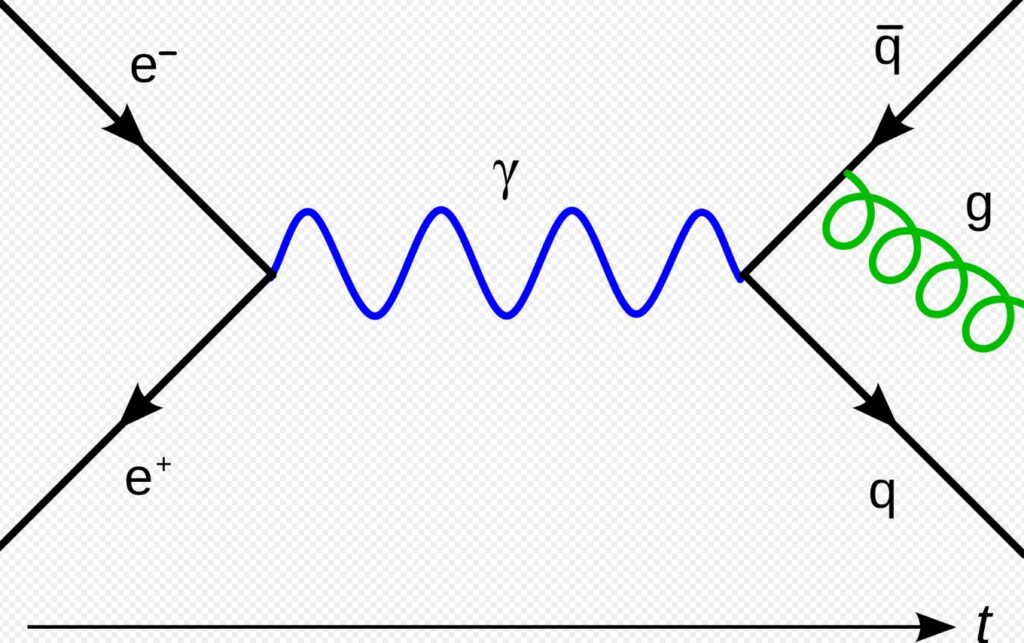
Quantum field theory (QFT) merges quantum mechanics with special relativity and is the framework behind modern particle physics. It treats particles as excited states in underlying fields, not isolated dots. QFT explains how forces like electromagnetism and the strong nuclear force work at subatomic levels. From the Higgs boson to antimatter, this theory helps describe nearly every particle interaction we can observe.