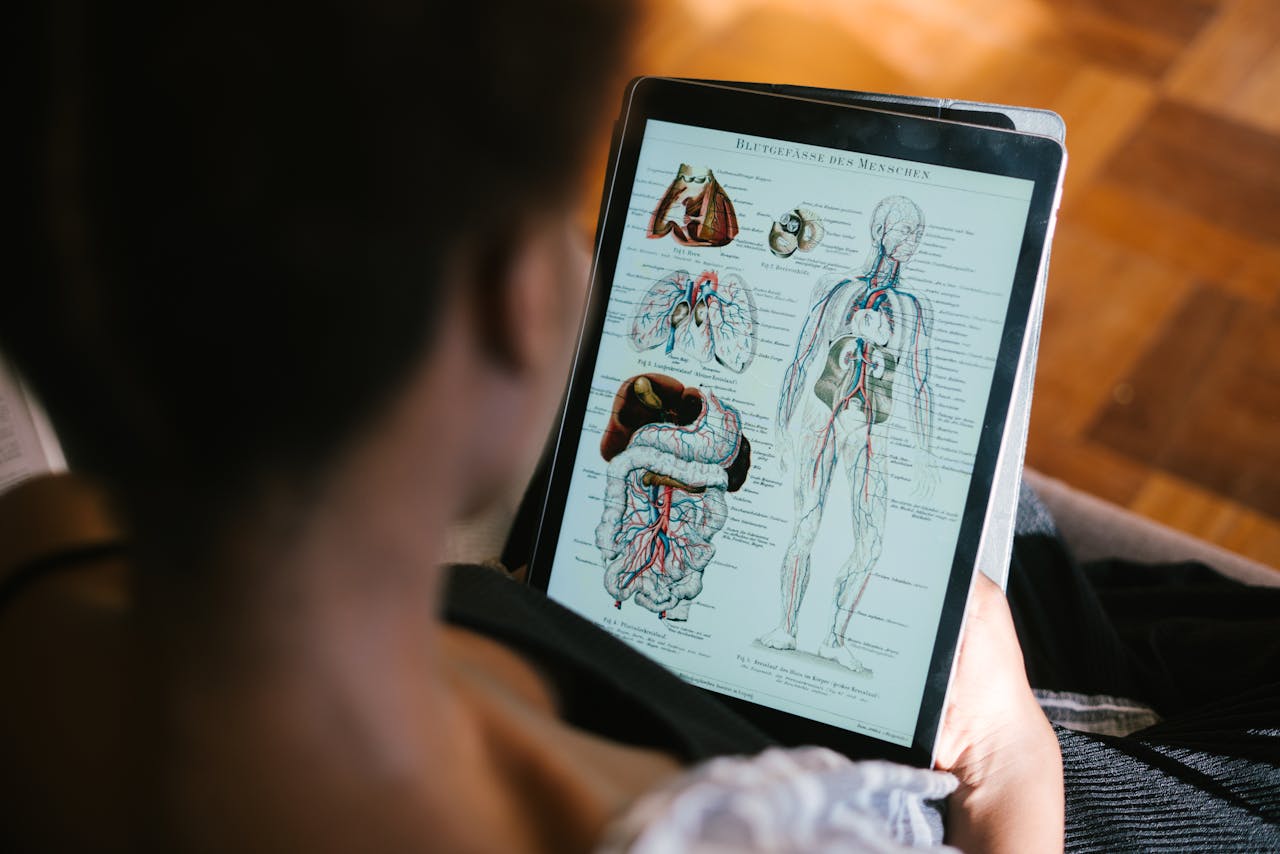
The human body is packed with surprises, many of which even teens in America may not realize. Beyond basic health class facts, there are hidden truths about how we function that can sound almost unbelievable. These details reveal just how extraordinary our biology is and show why modern medicine continues to unlock mysteries. From the brain’s energy use to the gut’s secret role, here are 10 surprising facts worth knowing.
1. Your Brain Uses About 20 Percent of Your Energy
Even though it makes up only around 2 percent of body weight, the human brain consumes nearly 20 percent of the body’s total energy. This high demand comes from the constant activity of neurons communicating and supporting vital functions. For American teens who might think sitting in class is passive, the brain is still working hard, even at rest. Doctors have studied oxygen and glucose use to confirm this, showing why staying nourished helps with focus. It explains why fatigue sets in when meals are skipped, since the brain never powers down.
2. The Gut Has Its Own Nervous System
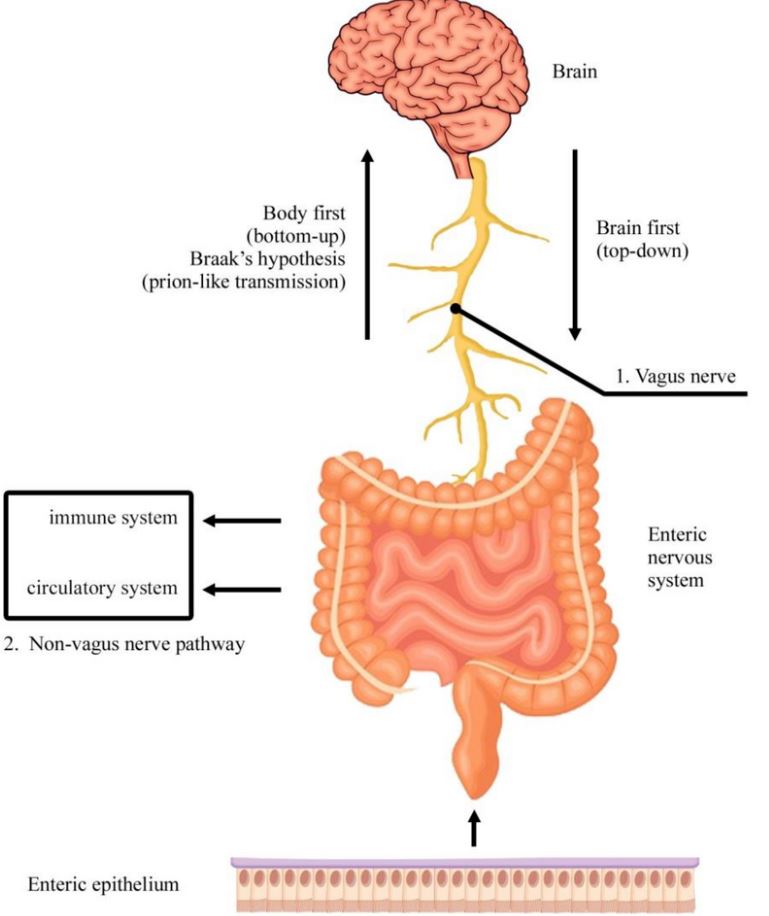
The digestive tract is more than a food processor. It has what scientists call the enteric nervous system, which contains millions of neurons that function somewhat independently of the brain. This “second brain” controls digestion and even communicates with mood-regulating centers. In the United States, research into gut health has exploded, especially as links between diet, mental health, and chronic illness become clearer. Teens often hear about probiotics or gut-friendly foods, but the reality is that this hidden system shapes how people feel and function daily.
3. Bones Are Stronger Than Steel
A cubic inch of bone can withstand more pressure than concrete and is stronger than steel by weight. While steel is denser, bone’s unique structure allows it to be incredibly resilient without being heavy. American doctors rely on this strength when repairing injuries, though bone can still break when force exceeds its limits. For teens, it is a reminder of why good nutrition and exercise matter, as calcium and vitamin D play key roles in maintaining this strength. Despite being living tissue, bones remain one of the body’s toughest materials.
4. The Stomach Replaces Its Lining Every Few Days
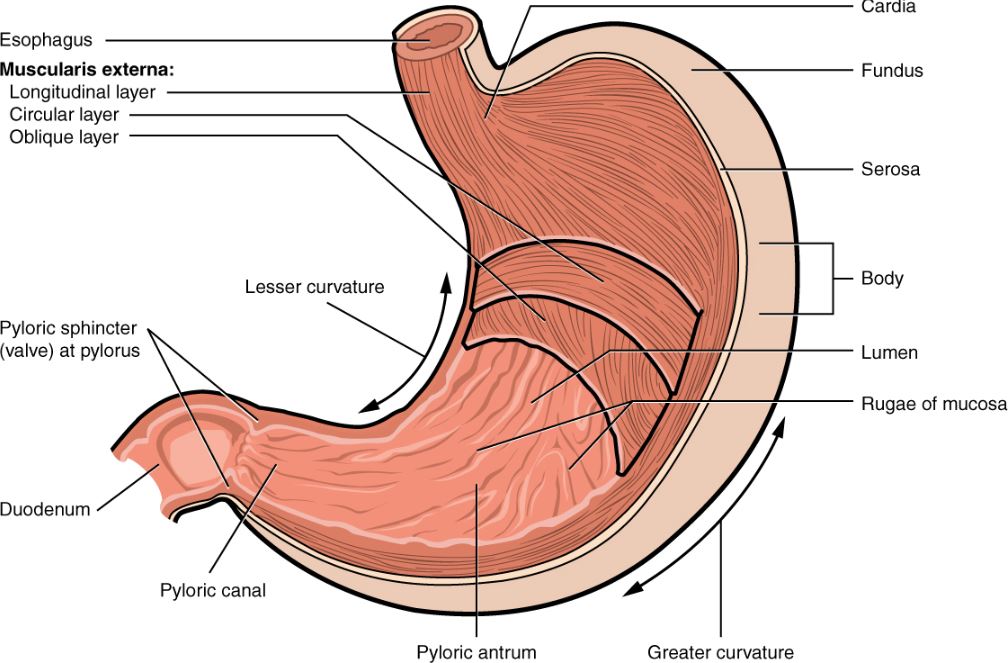
Acid in the stomach is strong enough to damage skin, yet the body keeps this power under control. The stomach protects itself by renewing its lining every three to four days, preventing self-digestion. Medical studies in the U.S. highlight how disruptions to this process, such as infections or poor diets, can lead to ulcers. Teens may overlook the stomach’s resilience, but this rapid cell turnover is a constant defense mechanism. Without it, eating the foods Americans enjoy daily would be dangerous, proving how adaptive the human body is.
5. Your Heart Beats Over 100,000 Times a Day
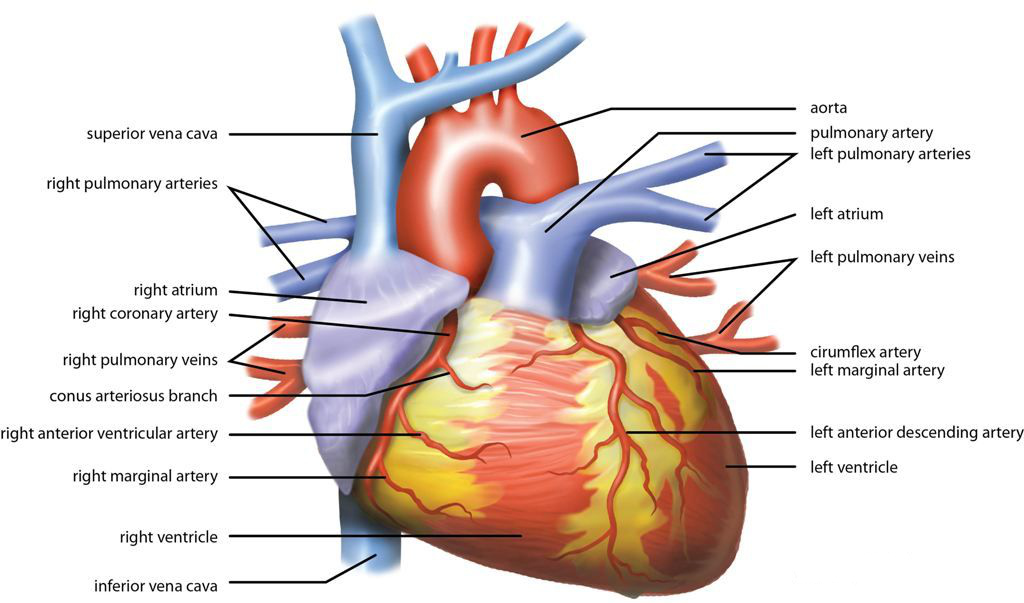
On average, the human heart beats more than 100,000 times every day, pumping oxygen-rich blood throughout the body. This nonstop motion keeps every system alive. In American medicine, heart health remains a leading focus since cardiovascular disease is the top cause of death. For teens, understanding this fact early encourages habits like exercise and avoiding too much processed food. It is not just an organ but a tireless muscle. Appreciating its workload shows why doctors emphasize maintaining healthy blood pressure and cholesterol even from a young age.
6. The Liver Can Regenerate Itself
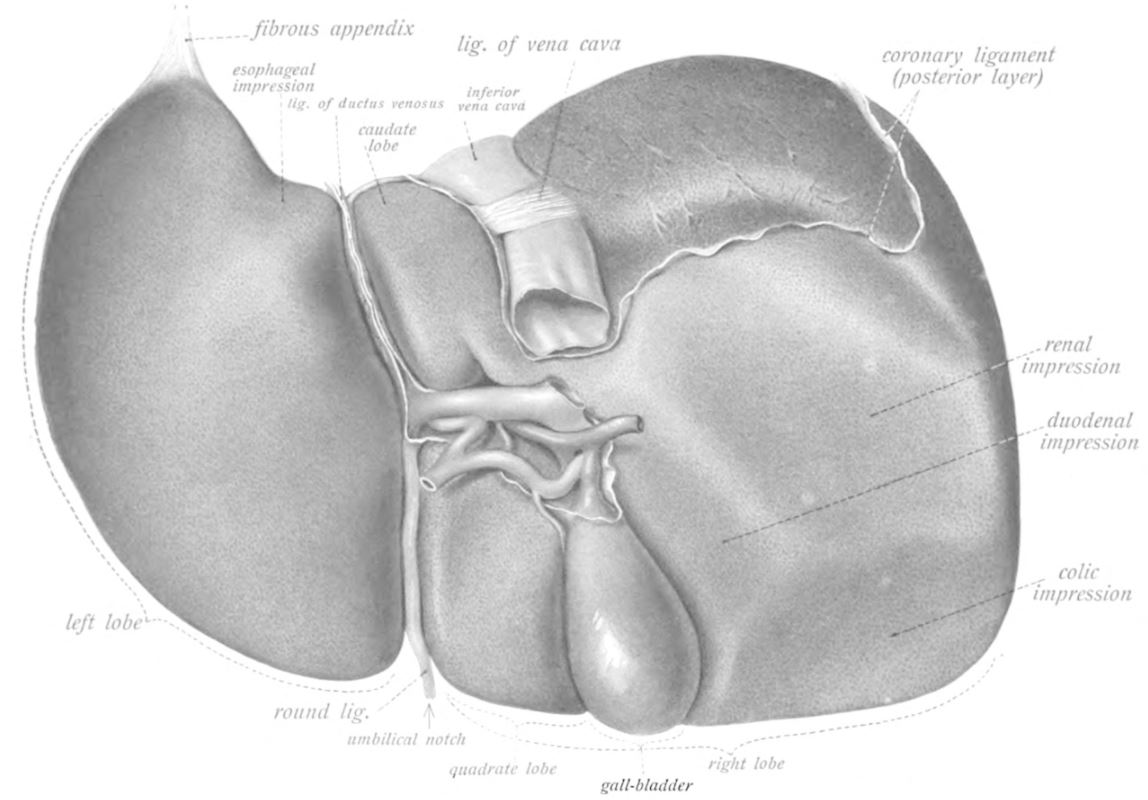
Unlike many organs, the liver has a remarkable ability to regenerate after injury or surgical removal of part of it. This regenerative capacity has been proven in countless medical cases in the U.S., where liver transplants and resections rely on it. The process does not mean instant healing, but new cells steadily restore lost tissue. For teens, it is an example of how the body has built-in resilience. However, it also highlights why avoiding alcohol or harmful substances is critical, since constant damage can overwhelm this natural repair system.
7. Fingernails Reveal Health Clues

Beyond their cosmetic role, fingernails can signal underlying medical issues. Doctors in America often look for changes like discoloration, ridges, or brittleness as clues to nutritional deficiencies, infections, or even heart and lung problems. This is why routine checkups sometimes include nail observation. For teens, this fact makes nail care more than just grooming. It is a reminder that the body communicates silently through subtle changes. Something as simple as pale or bluish nails could point to circulatory issues, showing how every detail of the body has diagnostic value.
8. Humans Shed Millions of Skin Cells Daily
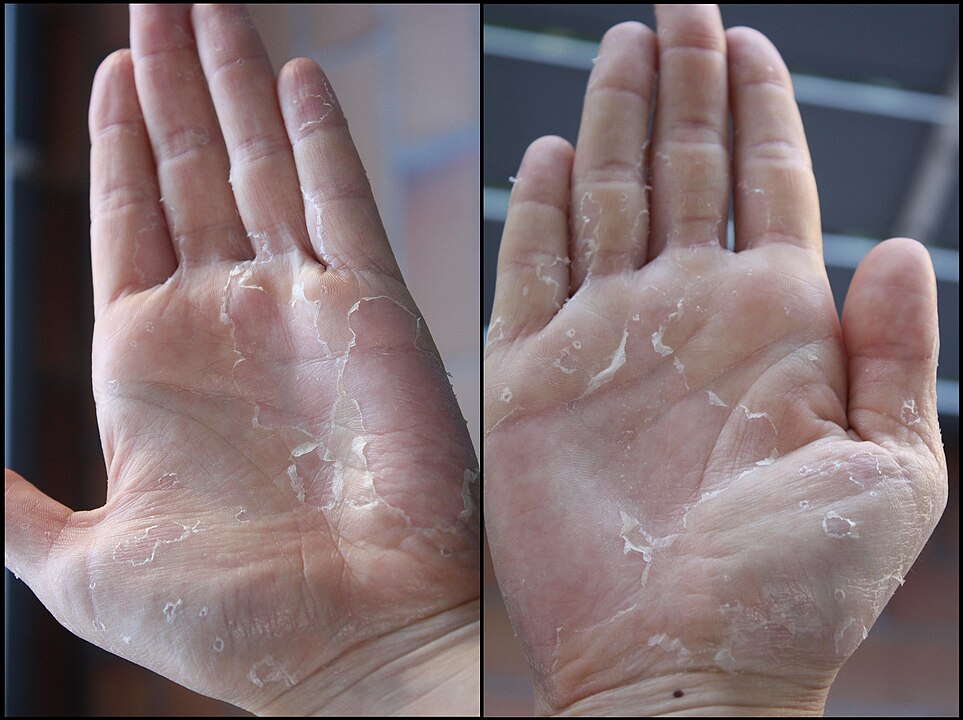
Every day, the average person sheds between 30,000 to 40,000 skin cells. Over a year, this adds up to pounds of material. While this may sound odd, it is part of the body’s natural renewal system. American dermatologists often stress skin health, reminding people that hydration, diet, and protection from sun exposure affect this cycle. For teens, it explains why skincare routines matter and why breakouts happen. Shedding skin also impacts the environment, as dust in homes contains much of this discarded material. It is biology happening in plain sight.
9. The Average Person Has About 60,000 Miles of Blood Vessels
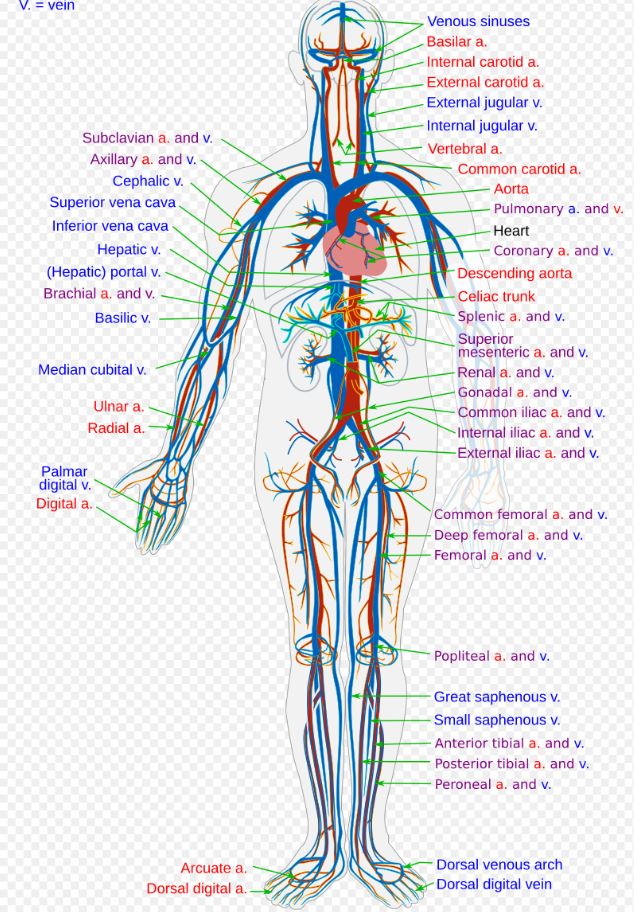
The human circulatory system is vast, with an estimated 60,000 miles of blood vessels in an adult body. If stretched out, they could wrap around Earth more than twice. This intricate network ensures that oxygen and nutrients reach every cell. In American medicine, studying circulation is key to treating conditions like strokes and heart attacks. For teens, it is striking to imagine how much is hidden beneath the skin, constantly at work. It demonstrates how tightly designed the human body is, balancing size and efficiency to sustain life.
10. Your Immune System Remembers Past Threats

The immune system has a memory that allows it to recognize and respond faster to infections encountered before. This principle is the foundation of vaccines widely used in the U.S. For teens, this means that childhood vaccinations continue protecting them through high school and beyond. Immune memory explains why many illnesses do not strike twice or are milder the second time. It shows how the body constantly learns from experience, like a built-in defense library. American public health efforts highlight this power to keep communities safe.