The human brain is the most complex organ we have, but many of its quirks never make it into classroom lessons. Beyond memory and problem-solving, it hides unusual traits that shape how we think, feel, and adapt. Some of these traits seem almost unreal until science explains them. These facts show a side of the brain that is surprising, sometimes puzzling, and always fascinating to explore.
1. Your Brain Generates Enough Electricity To Power A Lightbulb
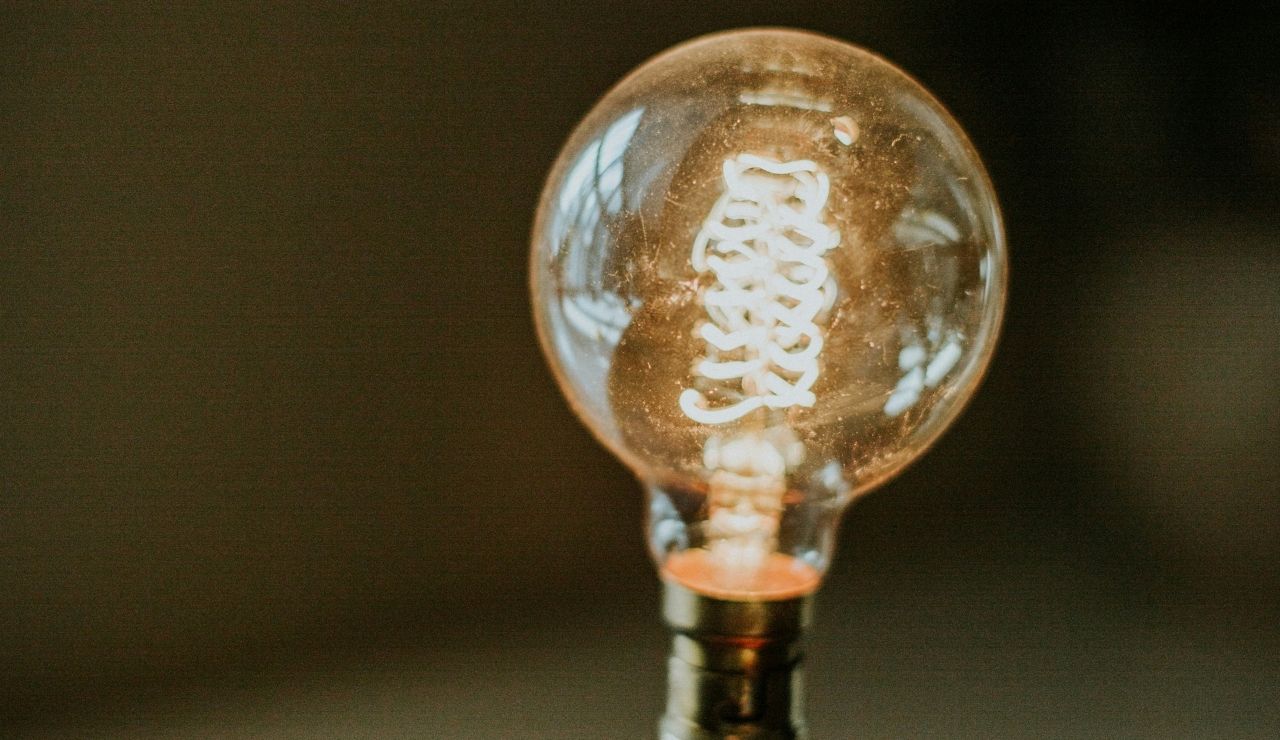

While active, the brain produces about 20 watts of electricity, enough to light a small bulb. Findings in Principles of Neural Science in 2021 explain that this output comes from billions of neurons sending electrochemical signals. These impulses control every action, from holding a conversation to recalling a distant memory. Without this constant electrical flow, even basic bodily functions and thoughts could not take place, highlighting the brain’s role as a living power source.
2. You Use More Than Ten Percent Of Your Brain
The long-standing idea that humans only use a fraction of their brains is false. Imaging studies in Nature Reviews Neuroscience in 2015 show that nearly every region becomes active over the course of a day. Even at rest, the brain maintains complex background operations, from storing experiences to regulating internal systems. This myth likely began when early researchers misread data, and it has been reinforced by popular culture rather than modern neuroscience.
3. Your Brain Has No Pain Receptors
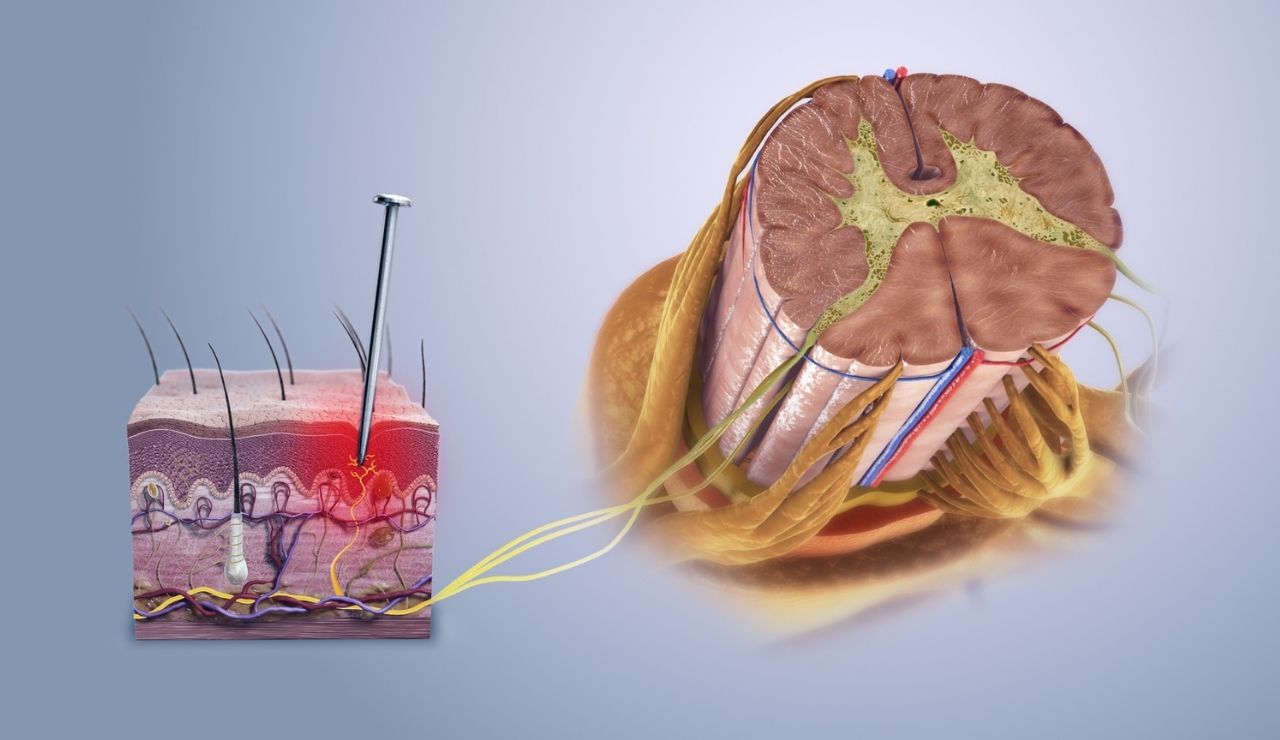
Though it processes pain signals from other parts of the body, the brain itself cannot feel pain. Nature Reviews Neuroscience in 2001 reported that this is because it lacks specialized nociceptors. Surgeons sometimes perform procedures on conscious patients after numbing the scalp and skull. When headaches strike, the discomfort comes from tissues, blood vessels, or membranes surrounding the brain, not the brain tissue itself, making this a surprising exception in the nervous system.
4. Dreams Are Linked To Memory Processing

Sleep is more than rest; it’s an active period of sorting, storing, and linking experiences. A review in Nature Reviews Neuroscience in 2013 suggests dreams may play a role in emotional regulation and memory integration. By weaving together events and feelings, the brain creates mental connections that strengthen recall. Consistent deep sleep supports these processes, helping improve problem-solving abilities and emotional balance during waking hours.
5. It Consumes A Lot Of Your Energy

Despite weighing only about three pounds, the brain uses roughly 20 percent of daily energy. The Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism in 2001 reports that this power fuels constant cellular activity and signal transmission. Even when at rest, the brain manages countless background tasks that keep the body running smoothly. Proper hydration, balanced nutrition, and adequate rest are essential to keep this high-energy organ functioning at its peak every day.
6. The Brain Cleans Itself While You Sleep

A network known as the glymphatic system works during deep sleep to flush out waste. Research in Science in 2013 found that it removes toxins built up during the day, including proteins linked to certain brain disorders. This cleansing cycle is most effective during uninterrupted rest, underscoring the importance of a consistent sleep schedule. Missing out on these hours may limit the brain’s ability to stay healthy over the long term.
7. Music Can Physically Change Your Brain

Engaging with music, whether learning to play or actively listening, can reshape brain structures. The Journal of Neuroscience in 2003 found that musicians often develop increased gray matter density and stronger neural connectivity. These changes enhance coordination, memory, and creativity. Even non-musicians benefit from exposure to music, as it stimulates multiple brain regions, promoting mood regulation and innovative thinking across different areas of life.
8. Multitasking Is Mostly An Illusion

What feels like juggling multiple activities is actually the brain switching focus repeatedly. The Journal of Experimental Psychology in 2001 found that this shift slows efficiency and increases mistakes. Concentrating on one task allows deeper processing and more accurate results. Despite the popularity of multitasking, the brain’s wiring favors sustained attention, making single-focus work the best way to achieve high-quality outcomes in less time.
9. Laughter Activates Multiple Brain Regions

Laughing triggers a network that includes motor control, emotion processing, and sound production areas. NeuroImage in 2003 showed that it also releases endorphins, natural chemicals that improve mood and promote social connection. This mix of neural activation and chemical reward helps explain why shared laughter builds bonds and reduces stress, benefiting overall well-being while encouraging positive relationships.
10. Smells Can Trigger Vivid Memories
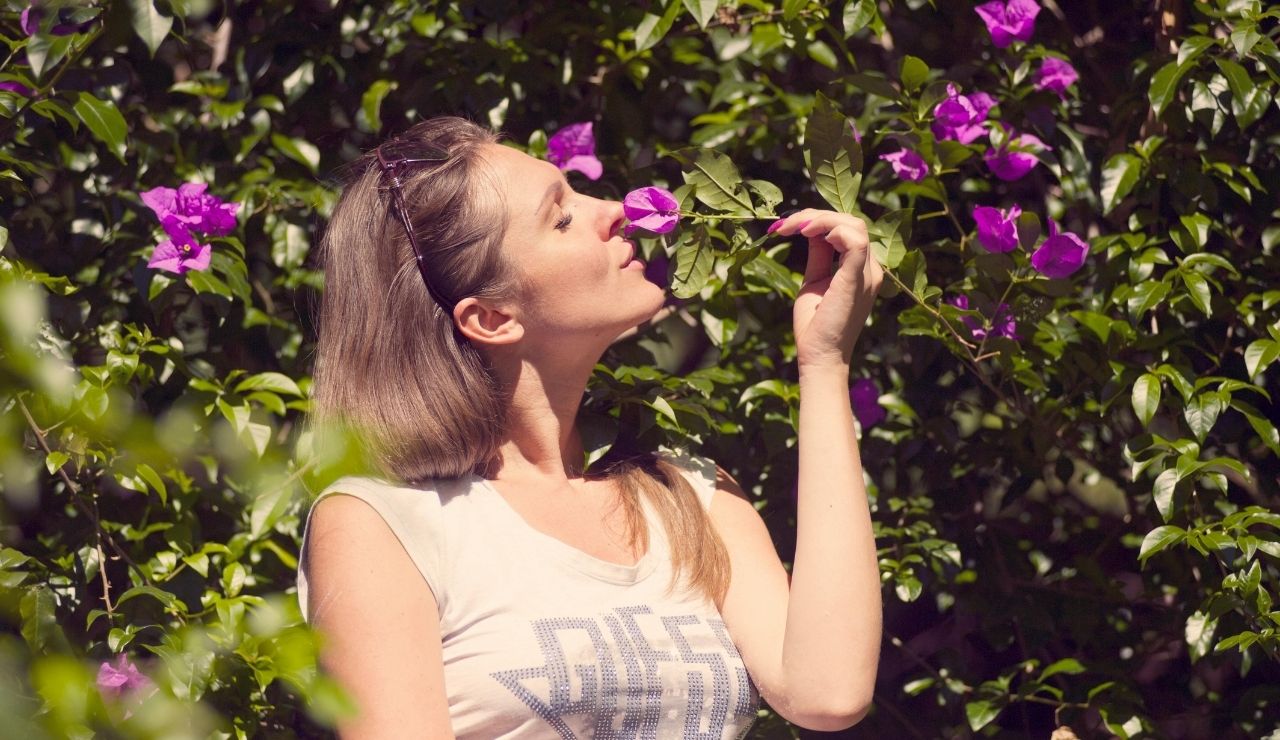

The olfactory system connects directly to brain regions tied to memory and emotion. Memory & Cognition in 1996 found that certain scents can instantly evoke detailed recollections, often carrying strong emotional weight. A familiar fragrance might bring back the atmosphere of a childhood home or a specific moment from years ago, showing how deeply scent is linked to personal history and emotional experience.